Geogrid Price
Geogrid Price varies largely based on factors like different types of materials, tensile strength, size of the apertures, types of coatings, and specific uses of the project. Being a cost-efficient geosynthetic product, geogrids have become the most popular in the works of soil reinforcement, road construction, slope stabilization, and foundation support, thus minimizing the expenses of the construction while at the same time, increasing the efficiency of the project during its lifespan.
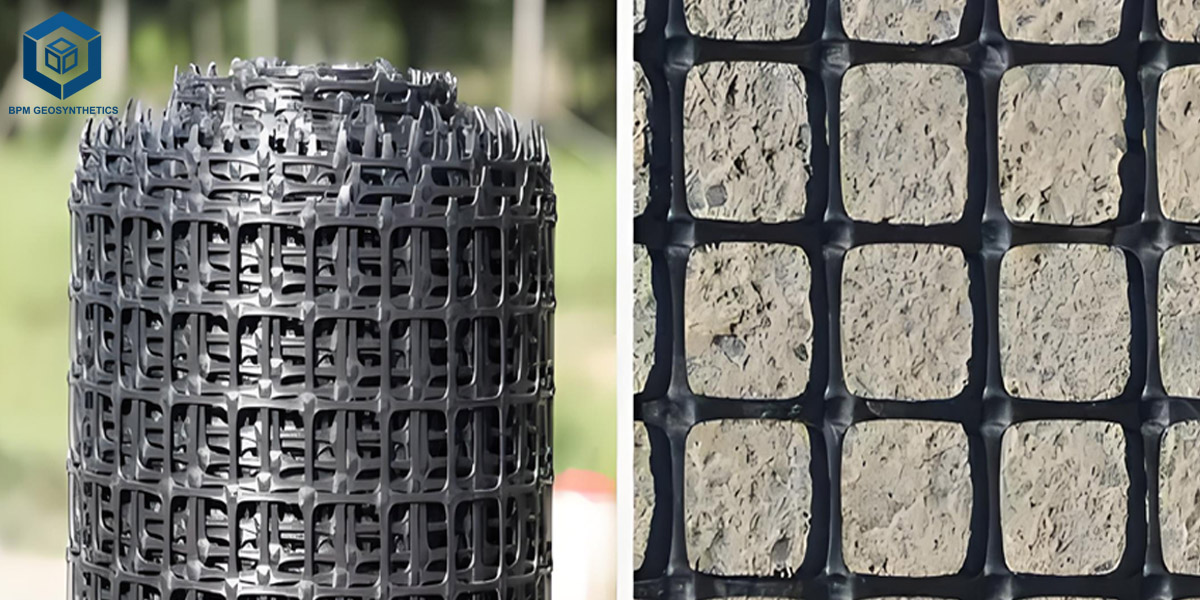
- Material Type: PP, HDPE, PET, fiberglass, or steel-plastic type of geogrids
- Tensile Strength & Specification: More robust and heavier grades are the cause of a higher price
- Manufacturing Process: Geogrids may be extruded, woven, or warp-knitted
- Application Area:roads, railways, retaining walls, slopes, or soft soil reinforcement
- Order Quantity & Customization: Unit prices go down with bulk orders and standard sizes
Choosing the right geogrid based on engineering requirements ensures optimal performance and the best geogrid cost per square meter or per square foot for your project.
Geogrid price depends on the integrated factors of material performance, structural design, manufacturing technology, and application specifics. Geogrid mesh being the primary geosynthetic materials for soil reinforcement are capable of providing the best load distribution, tensile strength, and long-term stability, thus, supporting the statement that they are a cost-effective alternative for infrastructure, civil engineering, and environmental projects.
1. Geogrid Types and Geogrid Price Differences
A number of different geogrid structures have a direct impact on the price level:
1.1 Uniaxial Geogrid Price
The hdpe uniaxial geogrid product is engineered to provide high-strength reinforcement in a single main direction only. In fact, this is the type of geogrid that is usually utilized in the construction of retaining walls and unstable steep slopes. Uniaxial geogrid is pretty straightforward that a higher tensile strength achieved in one single axis will be accompanied by a higher unit cost.
1.2 Biaxial Geogrid Price
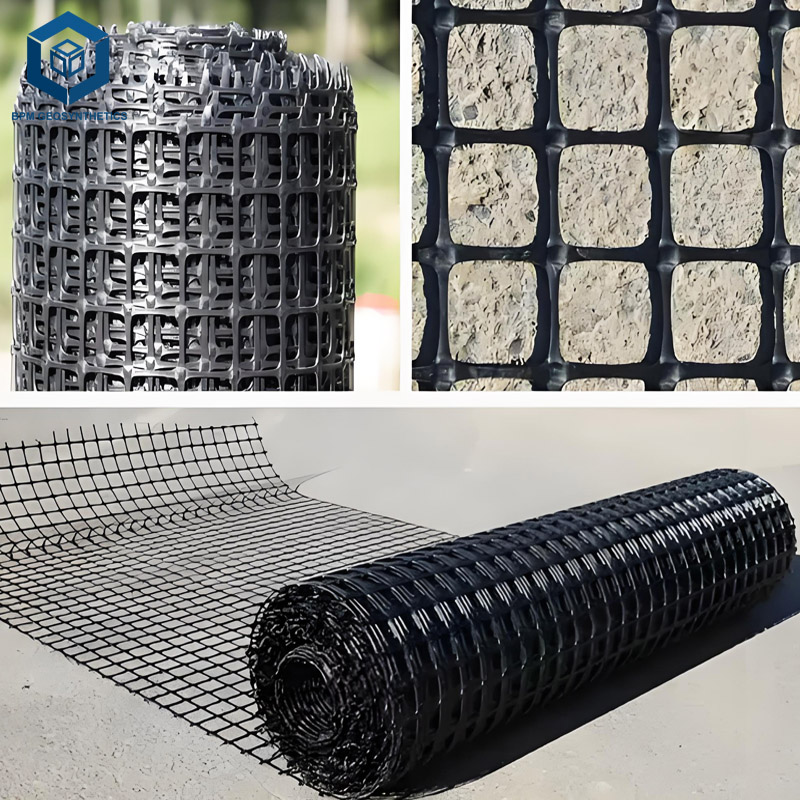
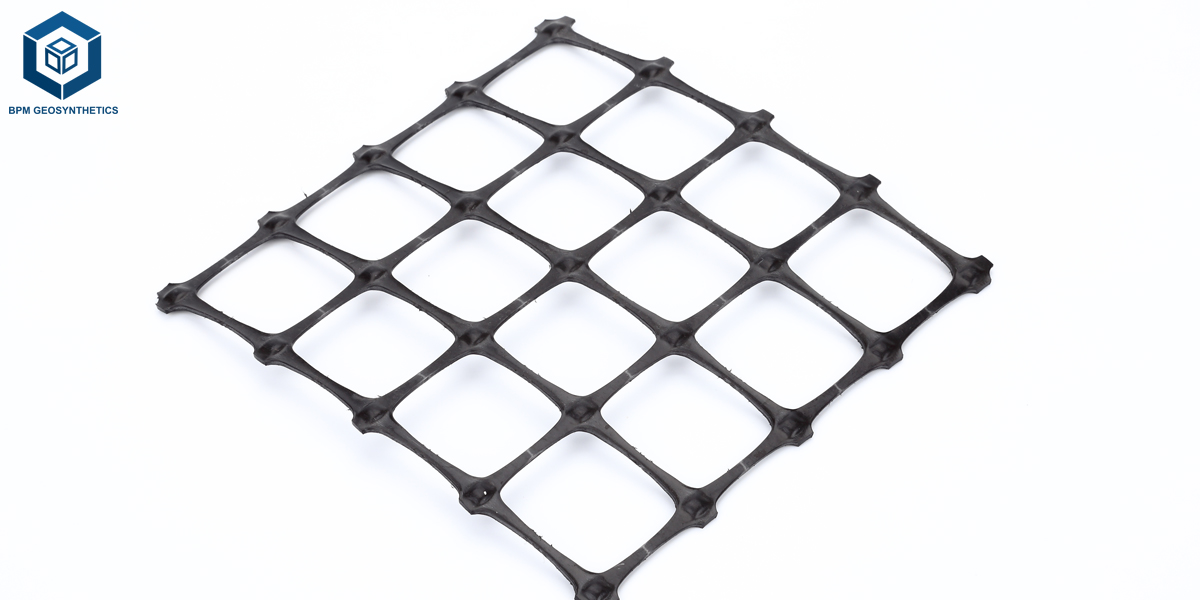
Balancing the strength in two directions, pp biaxial geogrid is the most widely applied type of the biaxial grid in the work of reinforcement of the road bases, pavements, and subgrade. PP geogrid has been a fact that this is the most budget-friendly and the mostly picked option.
1.3 Triaxial Geogrid Price
This type of triaxial grid has 3-axes load distribution and is therefore the most suitable for heavy-duty roads as well as for the foundations of soft soil. The existence of advanced components and high-level performance makes it a bit pricey in comparison with others.
2. Material Composition and Geogrid Price Cost Impact
The constituent material of geogrid is one of the most important factors that influence not only the price but also the performance and the lifespan of the product:
2.1 PP (Polypropylene) Geogrid
Weighing less, being corrosion-resistant as well as cheaper than most of the other materials, thus, making it the perfect choice for general soil reinforcement, road subgrades, and landscaping when one puts a higher priority to economic efficiency.
2.2 HDPE Geogrid
Characterized by superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and long-term durability, HDPE geogrid is the best choice for projects situated in extremely harsh environments, such as landfills, mining areas, and coastal areas, notwithstanding the fact that it is offered at a moderate price level.
2.3 PET (Polyester) Geogrid
High tensile strength and very low creep under sustained loads are the first two properties that come to mind when one thinks of PET. The pet geogrid material is used mainly for embankments, retaining walls, and reinforcement of the foundations of high-load capacities. The price of the product is usually higher though, than PP and HDPE.
2.4 Fiberglass Geogrid
Glass fiber geogrid is characterized by a high elastic modulus and exceptional thermal stability, thus often used for the reinforcement of asphalt pavements with a view to preventing the development of cracks and ruts. At the same time, this results in a relatively increased fiberglass geogrid material cost.
2.5 Steel-Plastic Geogrid
On the one hand, the steel plastic geogrid product is the combination of the high-strength steel wire with protective polymer coatings. On the other hand, the product delivers a high load-bearing capacity and structural reliability for heavy-duty projects. It is placed at the higher end of the price range.
3. Technical Specifications and Geogrid Price Correlation
Geogrid price usually rises when the technical performance level goes up and the engineering requirements become even more demanding:
3.1 Tensile Strength
When it comes to increasing tensile strength values (kN/m), it goes hand in hand with the need for more raw materials and higher level of manufacturing control. This leads directly to an increase in production costs. On the other hand, this allows the reinforcement at the load to be stronger and better distributed.
3.2 Aperture Size & Stability
Terracing the carrying and clothing of soil tightly and making the geometry very stable increases the efficiency of the structure, yet it is necessary to use more precise equipment and quality control which will result in a higher price per unit.
3.3 Coating & Treatment
To improve chemical resistance, UV resistance, and to ensure the durability of the product during installation, PVC, bitumen, or polymer coverings may be used. However, this necessitates extra processing operations which affect the final geogrid price.
3.4 Creep Resistance & Service Life
Geogrid material that produce very little creep and are designed for long-term load-bearing applications utilize materials that are of a higher grade and have testing standards that are more rigorous. Consequently, they become more expensive upfront, but the total cost of maintenance and operations over the lifespan of the product is significantly decreased.
4. Application-Based Geogrid Price Considerations
Each engineering application has specific requirements for the type of geogrid that must be used, which consequently has a direct impact on the level of pricing that can be expected:
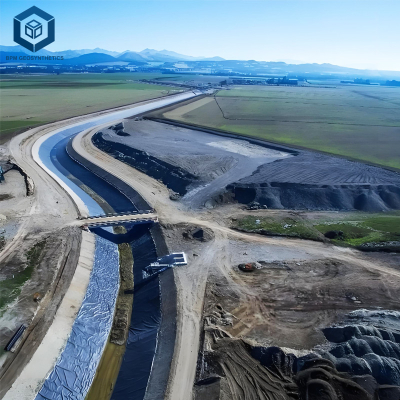
4.1 Road & Highway Construction
Medium to high-strength biaxial geogrids work best in terms of the necessary trade-offs between load distribution, base material reduction, performance, durability, and total project costs.
4.2 Railway & Airport Foundations
In these projects, the use of high-strength, low-creep geo grid for gravel that tightly adhere to technical and safety standards is a must, thus resulting in pricier products that however guarantee not only stability but also safety even under heavy dynamic loads.
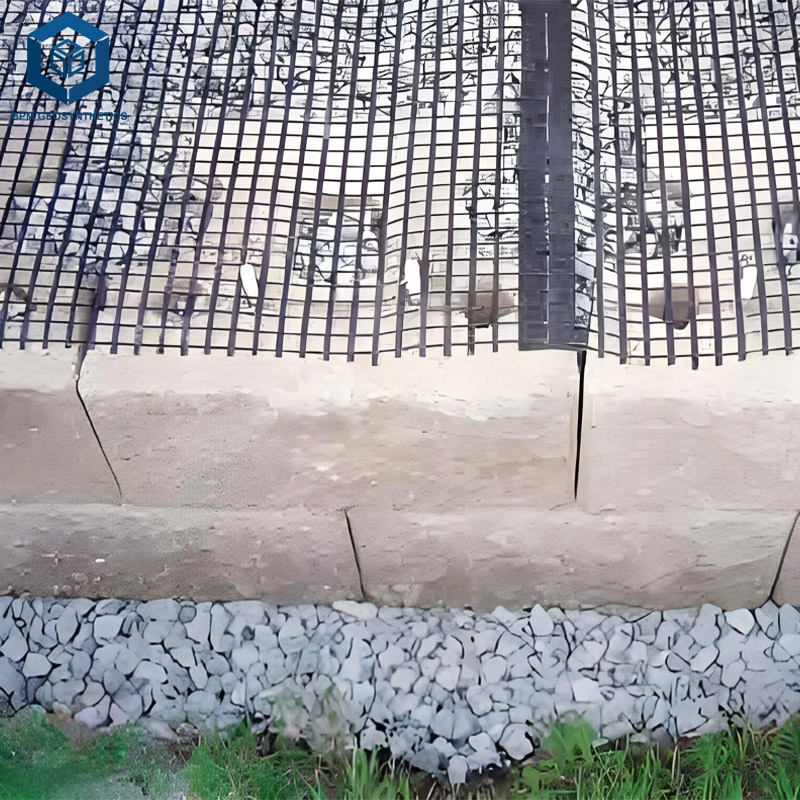
4.3 Slope Stabilization & Retaining Walls
The geo grid for retaining wall materials used for the application would generally be uniaxial or steel-plastic geogrids that have a very high tensile capacity and therefore, they are suitable for resistance against lateral earth pressure/ the outcome is that there will be an increase in the cost of the material due to the improvement in the strength and performance of the anchoring
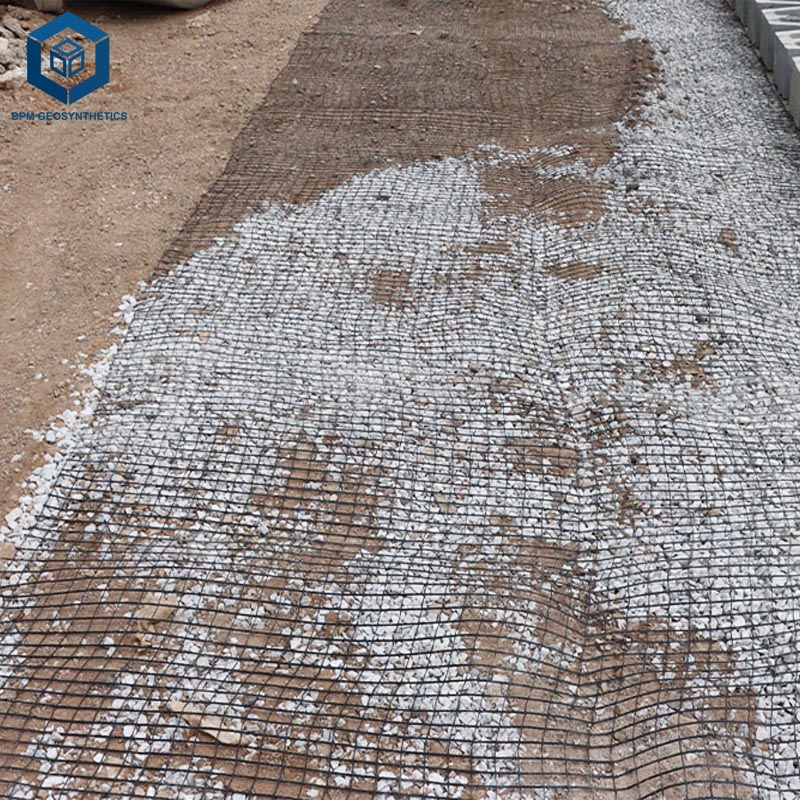
4.4 Soft Soil Reinforcement
Triaxial or high-performance geogrids provide exceptional confinement and stress transfer to weak subgrades. Therefore, geogrid soil stabilization require a higher initial investment, but they offer a better long-term return on investment and lower maintenance costs.
5. Geogrid Price Units and Measurement
Geogrids are usually priced by:
Cost per square meter (m²) – most common for international projects
Cost per square foot (ft²) – often used in North American markets
Cost per roll – suitable for bulk procurement and logistics planning
6. Geogrid Order Quantity, Customization & Supply Factors
Several factors such as order quantity, level of customization, and supply conditions significantly influence the final geogrid price:
6.1 Bulk Orders
When purchasing in large volumes, the manufacturers can take advantage of economies of scale regarding raw material procurement and production processes. This results not only in lowering the unit price but also in more competitive project-level costs.
6.2 Custom Specifications
Specifications like special tensile strength grades, non-standard roll sizes, particular colors or unique coating may require some additional setup and quality control, thus the overall cost might increase a bit.
6.3 Factory-Direct Supply
If someone buys directly from the geogrid manufacturers they are able to do away with the intermediate markups and are thus guaranteed a consistent product quality while also gaining better negotiating power on delivery time, technical support, and after-sales service.
6.4 Logistics & Location
Aside from the freight charges, which are determined by the distance of the journey, export packaging standards, method of container loading, and delivery options, the final landed cost that will be faced by the project at the site is also influenced.
7. Geogrid Price Effectiveness & Long-Term Value
It may be that the initial price of geogrids varies; yet top-notch geogrids are capable of bringing about big economic and engineering advantages in the long run:
7.1 Reduced Aggregate Thickness and Excavation Volume
By efficiently confining the soil and distributing the load, the need for thicker base layers and extensive excavation is eliminated, which means a direct reduction in the usage of materials as well as construction expenses.
7.2 Lower Maintenance and Repair Costs
Geogrid erosion control improve the stability of the structure and reduce deformations. Therefore, they minimize the occurrence of such problems as rutting, cracking, and settlement. Hence, the number of repairs will be low throughout the lifespan of the project.
7.3 Extended Service Life of Roads and Foundations
Better reinforcement performance allows the infrastructure to resist repeated loading and the effects of the environment, thus their operational life (e.g., of roads, embankments, and foundations) is lengthened.
7.4 Improved Structural Safety and Performance
By increasing the load-bearing capacity and overall system integrity of the structures, geogrid ground grid provide a safer, more reliable source of energy to the structures with consistent performance under long-term and heavy-use conditions.
Conclusion
The choice of the perfect geogrid is not mainly about choosing the cheapest one, but rather matching its technical performance with the exact project requirements. A geopgrid correctly chosen will give the highest reinforcement efficiency, the structure's long-term stability, and the lowest total lifecycle cost, thus, it is a wise and eco-friendly investment in today's infrastructure and geotechnical engineering projects.
When it comes to quality, competitive pricing, and professional technical support, The Best Project Material Co., Ltd.(BPM Geosynthetics) is the manufacturer and supplier which one can be trusted, and it is ready to provide a complete line of geogrid solutions which can be adapted to various engineering applications all over the world.