What Are the Main Applications of Geogrid?
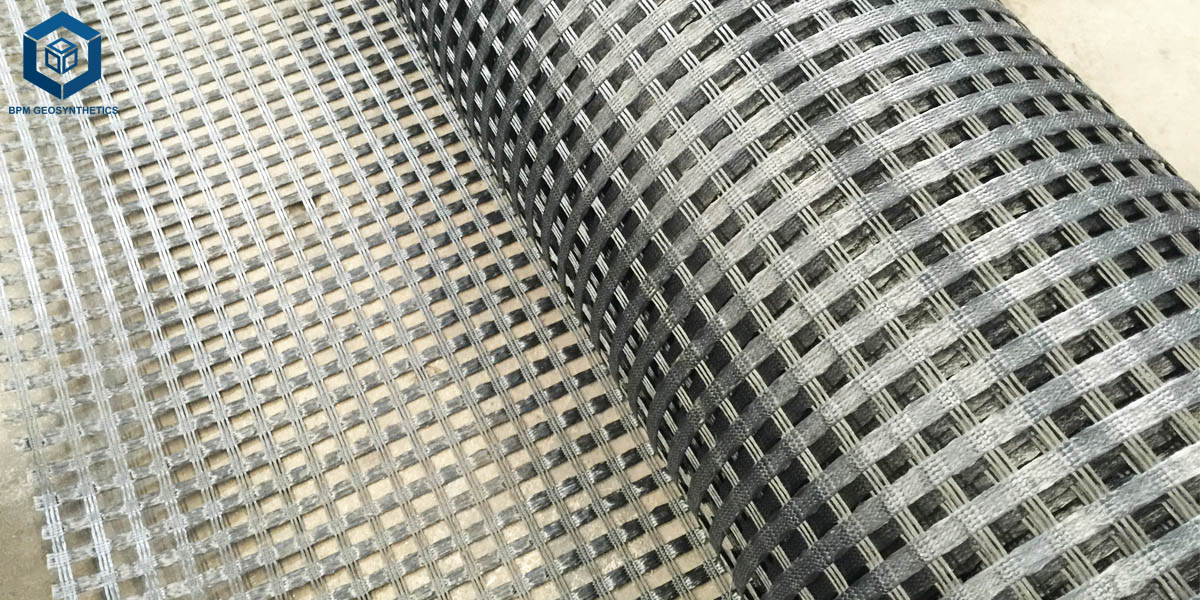
A geogrid is a kind of geosynthetic fabric frequently utilized in civil engineering and development for functions such as soil reinforcement, floor stabilization, and load distribution. Typically manufactured from high-strength polymers like polyester, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), or fiberglass, Plastic geogrid is characterised via their open, mesh-like structure, which permits soil particles to interlock with the grid. This interplay considerably improves the mechanical overall performance of the soil, bettering its energy and stability.
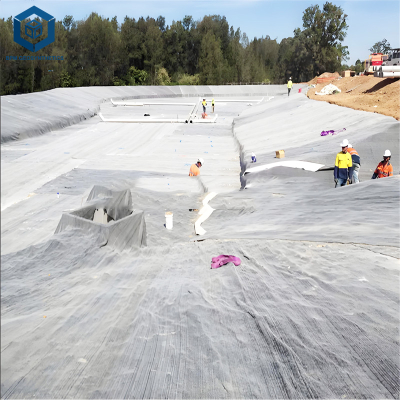
Due to their excessive sturdiness and efficiency, geogrid is drastically utilized in roadways, maintaining walls, slope protection, and erosion manipulate systems. They provide a inexpensive and long-lasting choice to standard reinforcement substances such as metal or concrete, making them a favored answer in current infrastructure projects.
1. What is Geogrid?
1.1 Structure and Composition of Geogrid
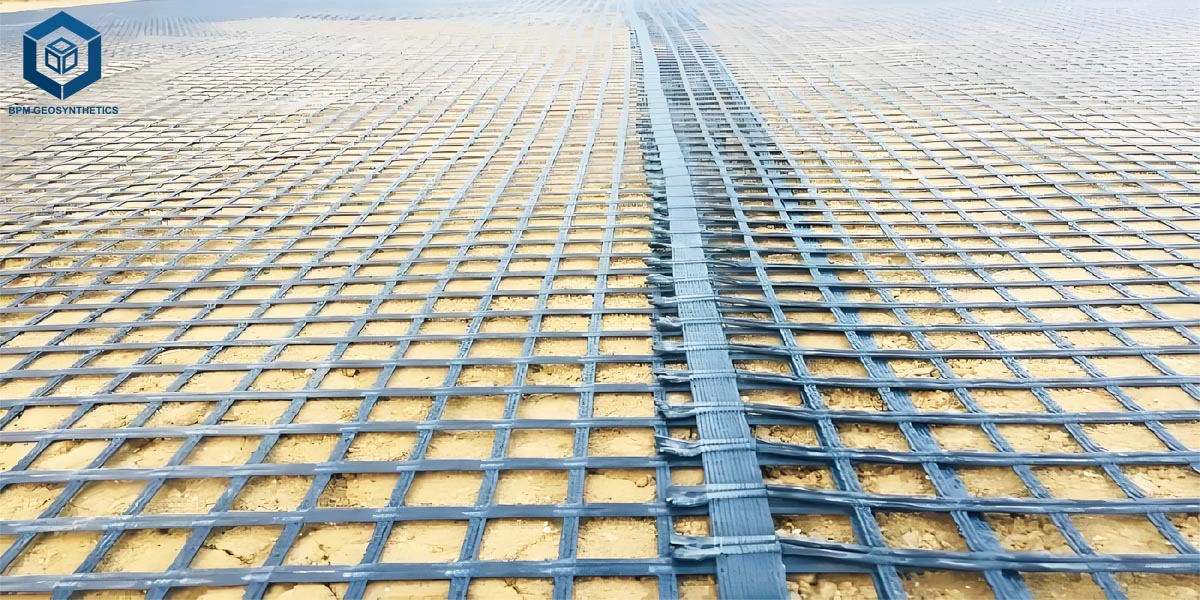
Geogrids are superior geosynthetic substances designed with a grid-like framework presenting giant apertures (openings). These apertures allow soil particles, aggregates, or different fill substances to omit thru and interlock with the geogrid structure. This interlocking motion types a secure composite system, notably enhancing the strength, load distribution, and balance of the soil–geogrid matrix.
1.1.1 Geogrid Core Structural Elements – Ribs (Longitudinal and Transverse)
The ribs are the main load-bearing participants of the geogrid, strolling in one or two instructions relying on whether or not the geogrid is uniaxial or biaxial. Longitudinal ribs lift tensile forces alongside the length, whilst transverse ribs grant balance throughout the width. Together, they make sure the plastic geogrid mesh can stand up to anxiety and distribute masses successfully in its supposed applications.
1.1.2 Geogrid Junctions (Nodes)
Junctions are the connection factors the place the longitudinal and transverse ribs intersect. These nodes are engineered to furnish excessive shear resistance and hold the structure and structural integrity of the geogrid beneath utilized loads. Strong junctions make sure that forces are correctly transferred between ribs, stopping structural failure in disturbing soil reinforcement projects.
1.1.3 Geogrid Apertures (Openings)
Apertures are the openings between the ribs, exactly sized to enable soil or combination to penetrate and lock into the grid. This mechanical interlock will increase friction between the geogrid and surrounding materials, enhancing bonding and stopping lateral displacement of the soil. The aperture geometry is tailor-made for unique applications, such as street stabilization, slope protection, or conserving wall reinforcement.
2. Types of Geogrid
Geogrids can be categorised based totally on their manufacturing process, cloth composition, and structural design, every kind presenting special homes appropriate for distinctive engineering applications.
2.1 Geogrid Classification by means of Manufacturing Process
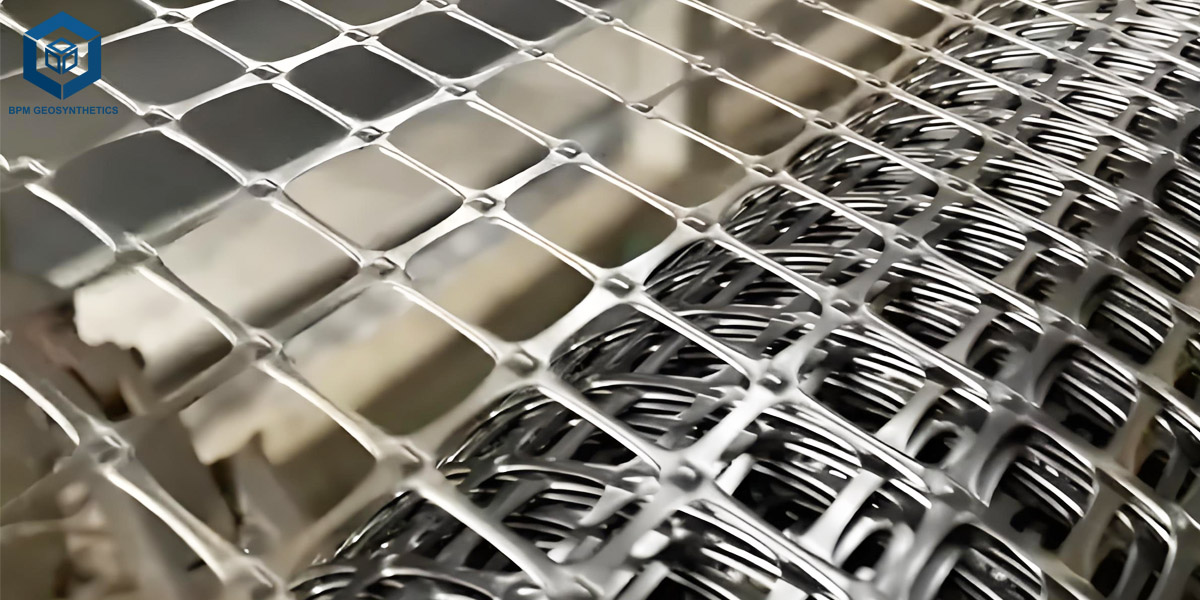
2.1.1 Extruded Geogrid
Produced thru extrusion and stretching of polymer sheets (HDPE or PP), growing a relatively oriented molecular shape for top-quality tensile strength.
2.1.2 Uniaxial Geogrid
Designed with excessive power in one predominant direction, making them perfect for keeping walls, steep slopes, and embankments the place unidirectional reinforcement is critical.
2.1.3 Biaxial Geogrid
Engineered for equal energy in each longitudinal and transverse directions, typically used in avenue base stabilization, parking lots, and basis reinforcement the place multi-directional load distribution is needed.
2.1.4 Woven or Knitted Geogrid
Manufactured with the aid of weaving high-tenacity polyester or fiberglass yarns into a grid pattern, then lined with a protecting polymer (e.g., PVC or asphalt).
Offers superb flexibility and fatigue resistance, making them appropriate for pavement reinforcement, railroad ballast stabilization, and asphalt overlay applications.
2.1.5 Bonded Geogrid
Constructed with the aid of lacing or welding polymeric ribs together, forming a inflexible grid structure.
Typically used in brief construction, erosion manage mats, and light-weight soil stabilization the place excessive tensile electricity is no longer required.
2.1.6 Triaxial Geogrid
Features a hexagonal or triangular aperture design, offering multi-directional load-bearing capacity.
Particularly high quality in high-traffic pavements, airport runways, and heavy-duty industrial flooring the place uniform stress distribution is essential.
2.2 Geogrid Classification by using Material Composition
- Polyester PET Geogrid: Known for its excessive tensile power and remarkable resistance to chemical degradation, making it perfect for long-term soil reinforcement.
- High Density Polyethylene HDPE Geogrid: Offers robust resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation and corrosion, making it appropriate for out of doors and buried applications.
- Polypropylene PP Geogrid: A light-weight and bendy material, regularly used in functions the place ease of set up is a priority.
- Fiberglass Geogrid: Exhibits very excessive tensile energy and is mainly used for asphalt pavement reinforcement due to its warmth resistance and low elongation properties.
Each fabric is chosen primarily based on elements such as soil type, load conditions, environmental exposure, and mission lifespan, making sure most excellent overall performance in various engineering scenarios.
3. Advantages of Geogrid
3.1 Geogrid - High Strength and Lightweight
Geogrids are designed to provide awesome tensile energy whilst final lightweight. In sure working conditions, their tensile power can even surpass that of metal reinforcement. Despite this strength, polyethylene plastic geogrid is convenient to handle, transport, and deploy due to their low weight, making them notably environment friendly for large-scale projects.
3.2 Geogrid - Economic and Material Saving
By enhancing soil steadiness and load distribution, geogrids can extensively limit the want for high-priced granular or combination fill materials. This optimization now not solely lowers cloth utilization however additionally reduces transportation costs, ensuing in full-size financial savings on general mission expenses.
3.3 Geogrid - Durable and Corrosion-Resistant
Geogrid is manufactured from wonderful polymers that furnish tremendous resistance to chemical corrosion, ultraviolet (UV) degradation, and organic tactics such as mould or bacterial attack. This ensures a lengthy carrier life, even in harsh environmental conditions, making them appropriate for everlasting infrastructure applications.
3.4 Geogrid - Convenient Construction
With their light-weight nature and proper flexibility, polypropylene geogrid can be effortlessly rolled out and located on-site except heavy lifting equipment. Their adaptability to distinct terrains and fast set up procedure assist decrease labor time and enhance development efficiency.
3.5 Geogrid - Green and Low-Carbon
Compared to normal concrete or asphalt reinforcement methods, geogrid-based solutions require fewer uncooked substances and much less strength to produce and install. This translates into decrease greenhouse gasoline emissions, making ground stabilisation grid a extra sustainable, environmentally pleasant desire for present day development projects.
4. Multi Scenario Application and Engineering Value of Geogrid
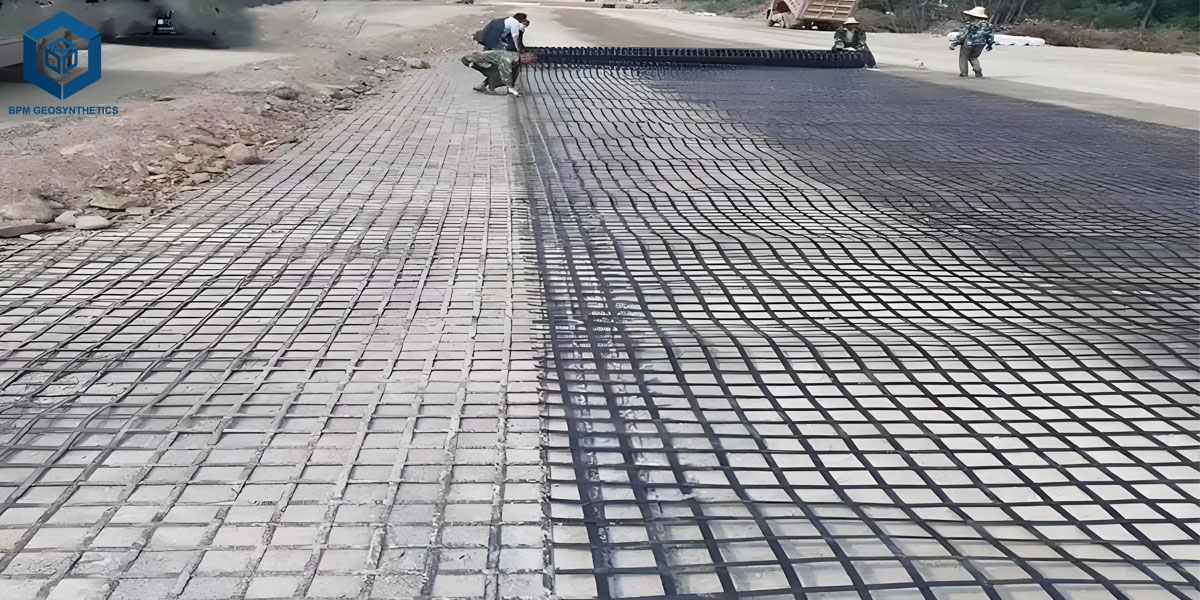
4.1 Geogrid for Roads and Airport Runways
• Soft basis treatment: laying two-way or three-way grids on silt, first-class sand or excessive liquid restrict clay can make bigger the bearing potential with the aid of 30% -60% and keep away from the phenomenon of "spring soil".
• Rut control: Adding fiberglass or composite grids underneath the asphalt floor layer can decrease the deformation of the tune belt by means of 40% -70% and prolong the preservation length through 2-3 times.
• Structural thinning: Through the layout of "equivalent thickness", the 40cm graded overwhelmed stone base is optimized to 25cm beaten stone+1-2 layers of high-strength polyester grating, saving 15% -25% in cost.
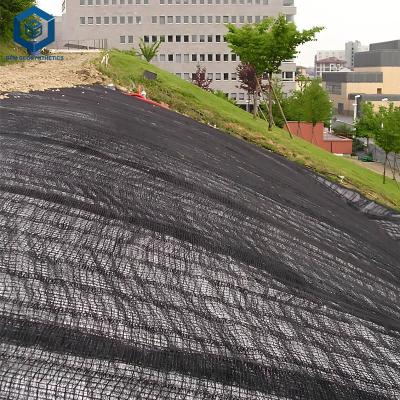
4.2 Geogrid for Retaining partitions and slopes
• Retaining wall: HDPE or PET grating is used as reinforcement, layered with graded overwhelmed stone, and the wall top can exceed 30 meters. Compared with concrete keeping walls, it saves greater than 50% of masonry work.
• Slope reinforcement: In a forty five ° -70 ° rock soil blended slope, a mixture of "lattice beams+two-way metal plastic grids+vegetation blankets" is used to extend the landslide security element by way of 1.4 instances and acquire fast slope greening.
4.3 Geogrid for Railway music bed
• Ballasted track: Laying PP welded grids with a tensile energy of 30-40 kN/m at the backside of the ballast can decrease the cumulative agreement brought about by means of instruct dynamic masses by way of 30% -50%, and limit the annual renovation frequency from four instances to 1-2 times.
• Transition part of ballastless track: Adjust the stiffness distinction with a grid geotextile composite layer to take away the phenomenon of "bridge jumping" and make certain the smoothness of high-speed trains jogging at 350 km/h.
• Heavy obligation railway: For sections with axle hundreds of over 30 tons, the use of grating and rubber cushion layer can minimize the pulverization charge of ballast through 60% and lengthen the carrier existence of the song mattress to 15 years.
4.4 Geogrid for Environmental Protection and Water Conservancy
• Landfill site: Cover a 200 kN/m high-strength PET geogrid on a 1.5 mm HDPE easy anti-seepage movie to stop contract and cracking of a 50 meter excessive pile; At the equal time, as a fuel conducting layer, it quickens the series of biogas.
• River financial institution protection: Using "gabion+bidirectional grid filter layer" as an alternative of regular masonry, the velocity of water injury restore is extended via four times, permitting for a 10 cm differential agreement of the financial institution slope except cracking.
• Seawall wave prevention: Combining polyester grating with concrete interlocking blocks, the tensile energy retention fee remains>80% after 20 years of carrier in a splash area with a tidal vary of four meters.
4.5 Geogrid for Agriculture and Landscape
• Terraced Fields on Slopes: A 20 kN/m polypropylene grid is laid on the 25 ° -35 ° slope of mountainous tea gardens to decrease soil erosion by means of 70%. Machinery can function on the mountain and amplify yield by way of 15% per mu.
• Three dimensional greening: A 30mm excessive convex factor drainage grille is brought to the base of the roof garden, lowering the weight by way of 120kg per rectangular meter and fixing the leakage hassle induced through overloading in typical methods.
• Temporary pasture: Install retractable fiberglass grid mats in muddy wetlands to grant transient roads for 20 ton forage transport machinery. After removal, vegetation will naturally get better inside two months.
Conclusion
This article systematically introduces the definition, structure, types, advantages, and software fields of HDPE geogrid, highlighting their key function in cutting-edge civil engineering. As a high-performance geosynthetic material, geogrid achieves soil reinforcement and load dispersion via a special grid structure, and is extensively used in fields such as roads, keeping walls, railways, and environmental engineering, with each monetary and environmental benefits.
BPM Geosynthetics is a China producer of geogrid materials. Through technological innovation and large-scale production, BPM geosynthetics has extensively decreased the manufacturing value of geogrids, presenting most economical options for infrastructure projects. In the future, with the development of science and intensified market competition, the price benefit of geogrids will be in addition highlighted, advertising their wider utility in the world engineering discipline and presenting robust aid for sustainable improvement goals.