Geocell Road Construction
In today’s global infrastructure landscape, geocell road construction has emerged as one of the most efficient and sustainable methods for soil stabilization and load support. With increasing demand for durable, low-maintenance road systems, geocell technology provides a cost-effective alternative to traditional road-building materials. Its cellular confinement structure offers superior strength, adaptability, and environmental benefits, making it ideal for highways, rural roads, mining access roads, and heavy-duty pavements.
Geocell Road Construction: Revolutionizing Modern Infrastructure
Introduction
In today’s global infrastructure landscape, geocell road construction has emerged as one of the most efficient and sustainable methods for soil stabilization and load support. With increasing demand for durable, low-maintenance road systems, geocell technology provides a cost-effective alternative to traditional road-building materials. Its cellular confinement structure offers superior strength, adaptability, and environmental benefits, making it ideal for highways, rural roads, mining access roads, and heavy-duty pavements.
This article explores the technological principles, market dynamics, and future trends driving the adoption of geocell road construction in the international civil engineering industry.
Understanding Geocell Technology
What Is a Geocell?
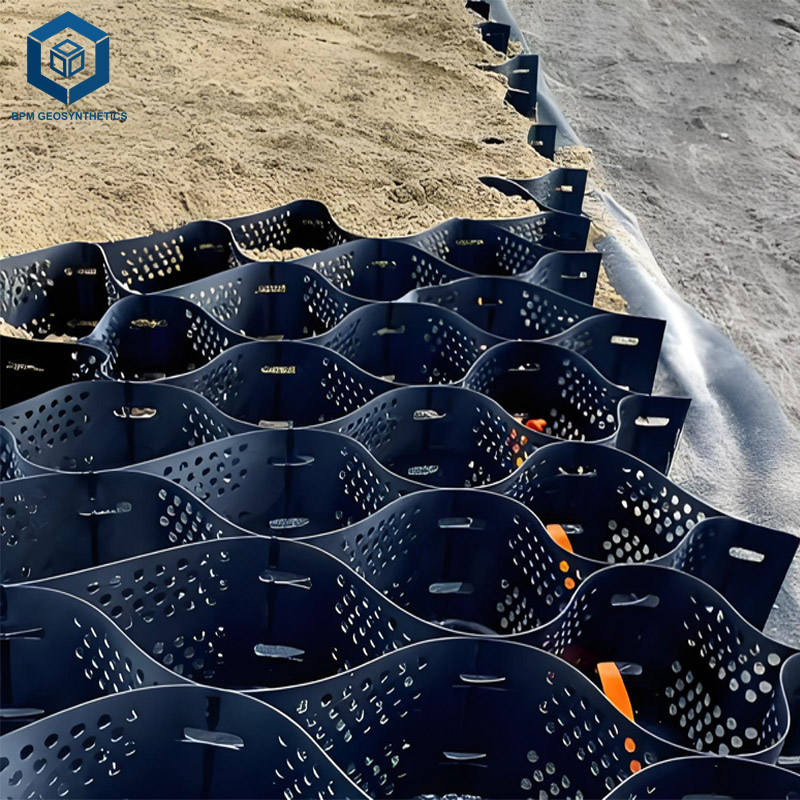
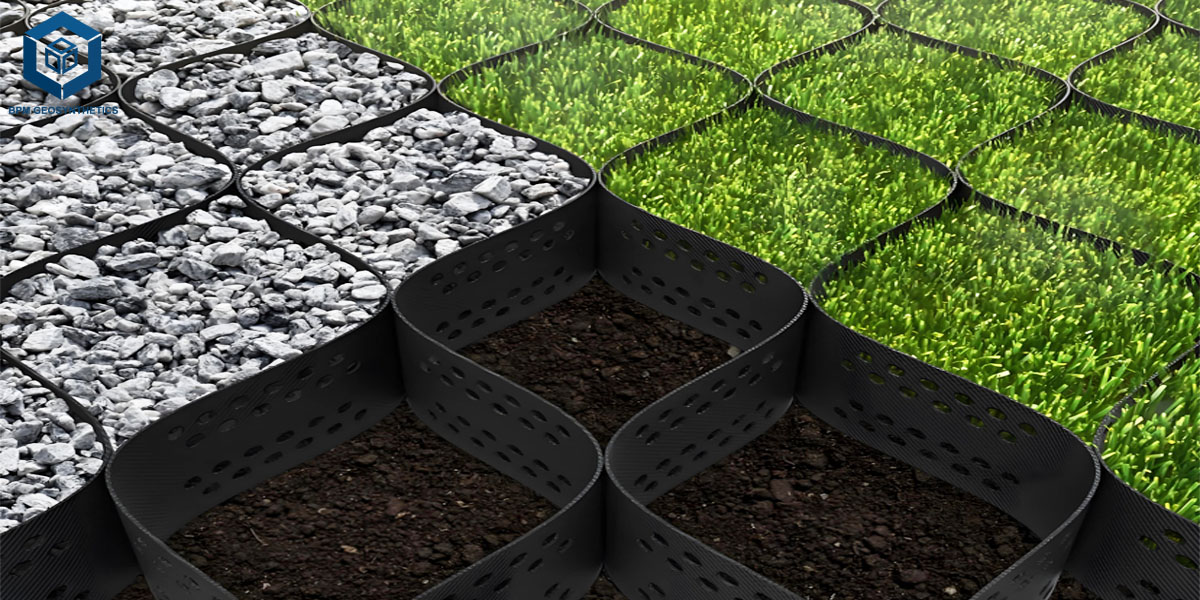
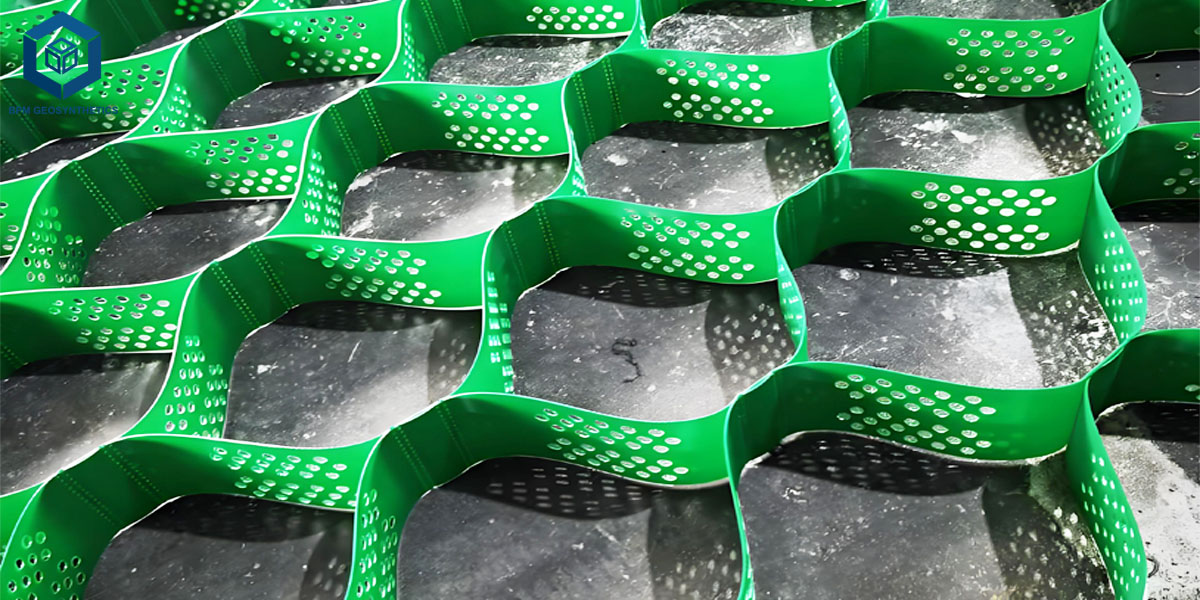
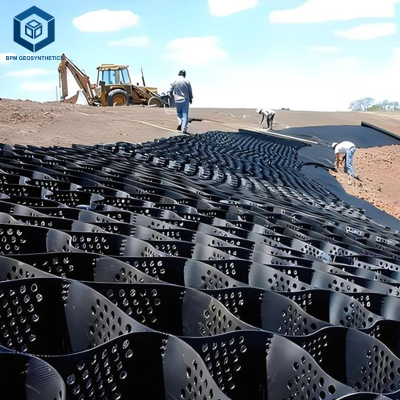
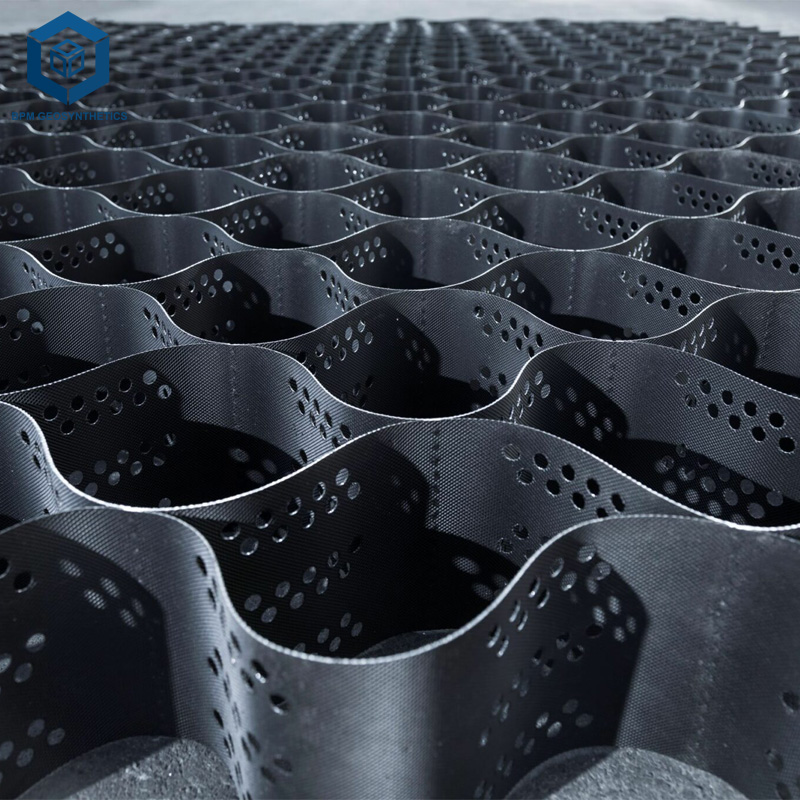
A geocell is a three-dimensional honeycomb-like structure made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or similar polymer materials. When expanded and filled with soil, gravel, or sand, it forms a stable cellular confinement system that enhances load distribution and reduces soil displacement.
The primary function of a geocell for road construction is to reinforce weak subgrades, prevent erosion, and extend pavement life. Its interlocking design resists lateral movement, providing structural integrity even under dynamic traffic loads or challenging environmental conditions.
Key Features and Advantages
Enhanced Load Distribution: Geocells distribute applied loads evenly across a wider area, reducing pressure on the subgrade.
Improved Soil Stability: They confine and reinforce loose soils, minimizing rutting and settlement.
Sustainability: Geocells allow the use of locally available fill materials, cutting down on carbon emissions and material costs.
Rapid Installation: Lightweight panels are easy to transport and deploy, reducing construction time and labor requirements.
Low Maintenance: Roads built with geocells require less frequent repair due to superior stress distribution and erosion control.
Market Overview and Growth Trends
According to recent market analyses, the global geocell road construction market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7% between 2024 and 2030. This growth is driven by rising investments in infrastructure modernization, the adoption of green construction materials, and the need for cost-efficient reinforcement systems.
Key Growth Drivers
Infrastructure Expansion in Developing Regions: Emerging economies across Asia, Africa, and South America are prioritizing long-lasting, low-cost road systems.
Environmental Regulations: Governments and agencies are encouraging sustainable materials in road construction to minimize ecological impacts.
Technological Advancements: Continuous innovation in polymer manufacturing has improved the strength and lifespan of geocell materials.
Reduced Lifecycle Cost: Compared with traditional stabilization methods, geocells offer up to 30% savings in total project costs.
Market Applications
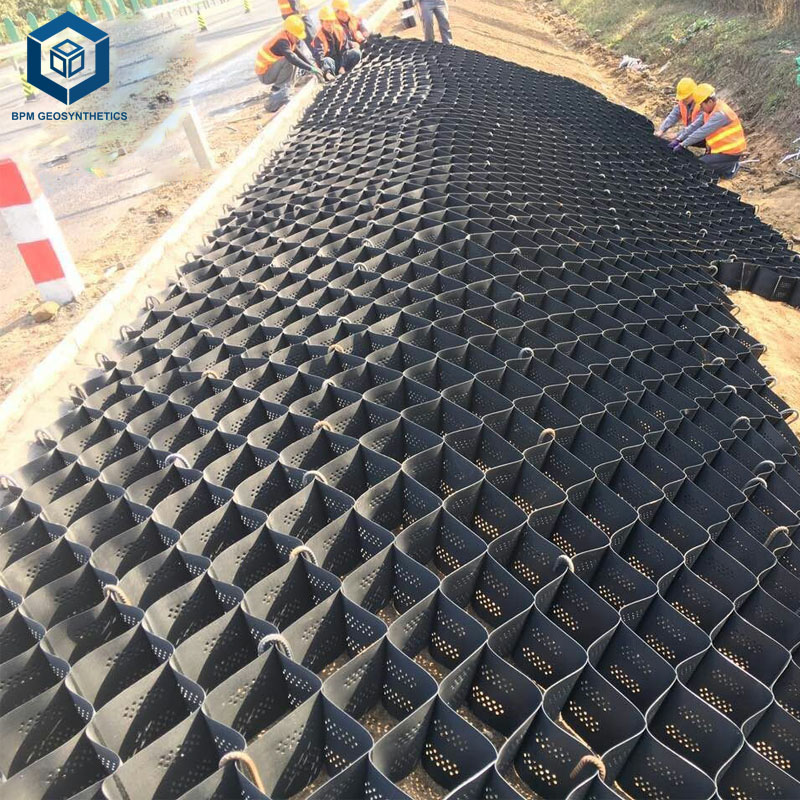
Highway and Railway Embankments
Access Roads for Oil, Gas, and Mining Sites
Slope Protection and Retaining Structures
Unpaved and Temporary Roads
Runways and Container Yards
Technical Aspects of Geocell Road Construction
Material Composition
Modern geocells are typically made from HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), known for its flexibility, chemical resistance, and UV stability. Some advanced products incorporate polyester or polypropylene for enhanced stiffness and bonding capabilities.
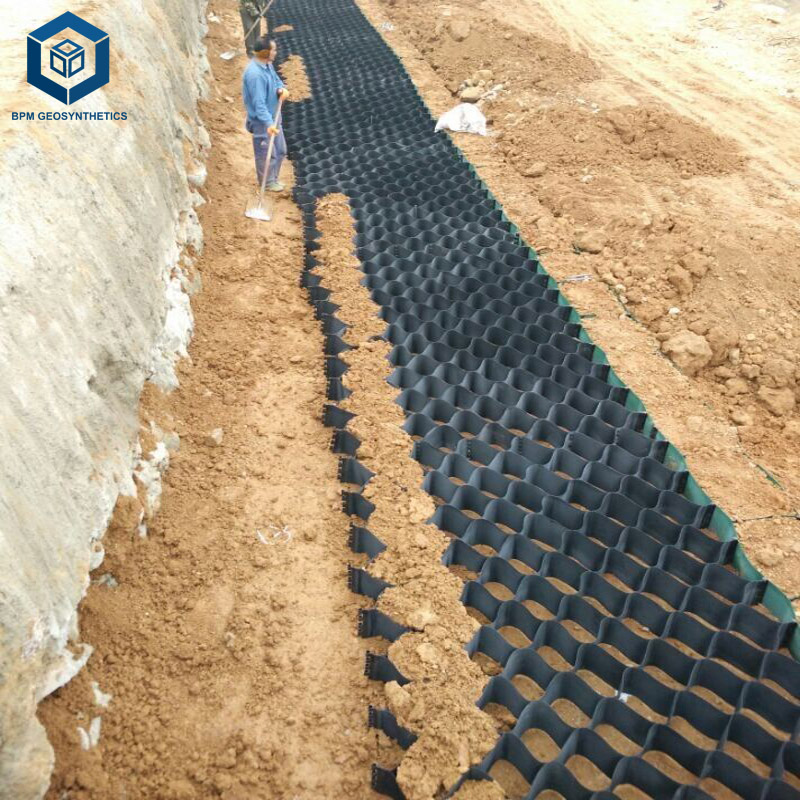
Installation Process
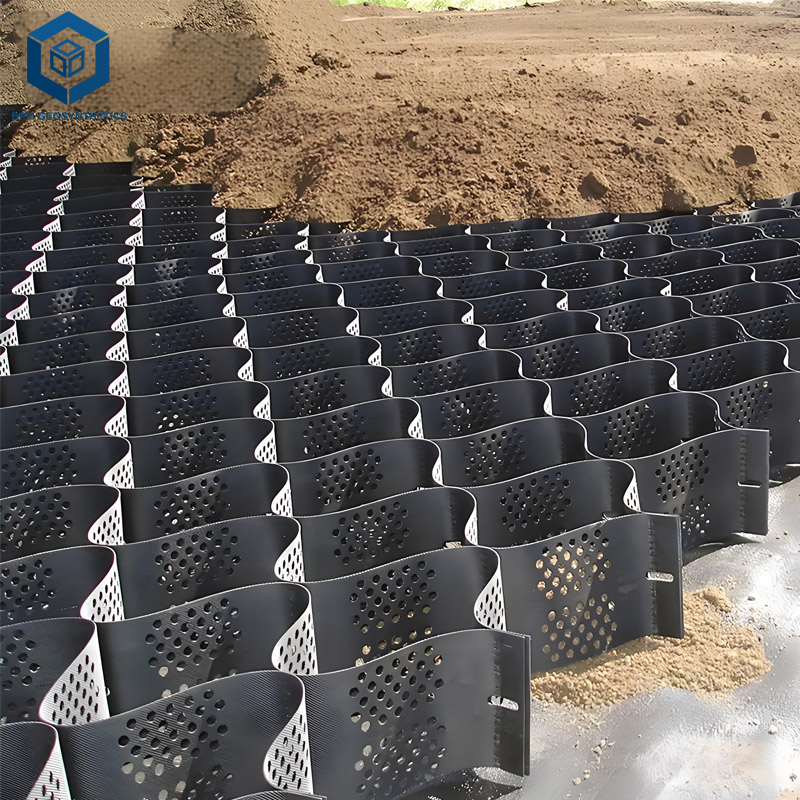
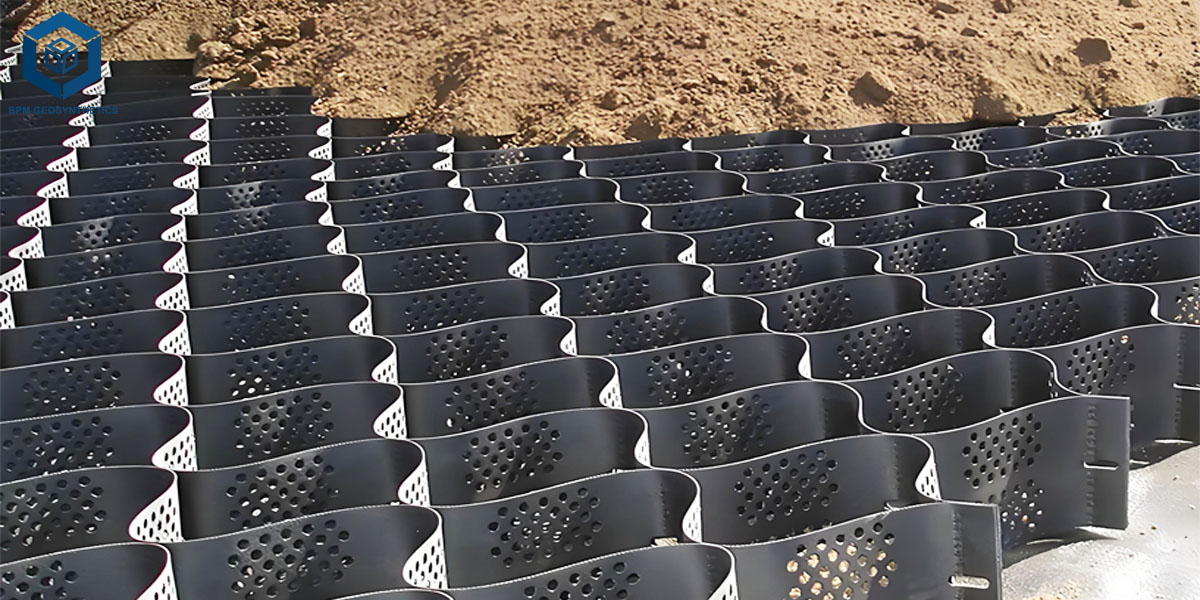
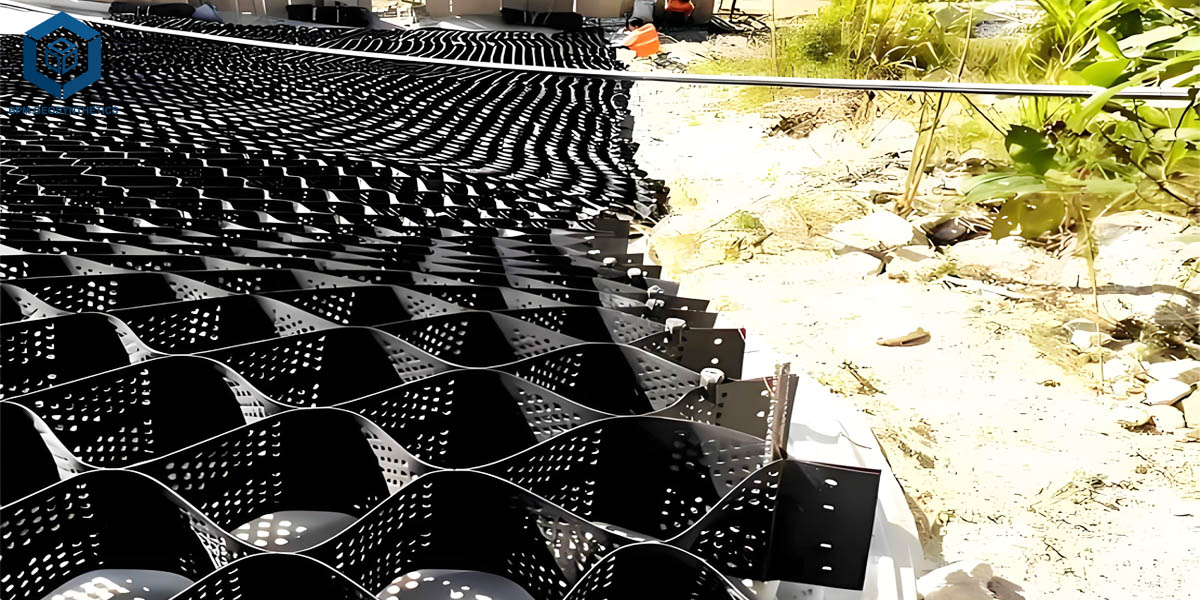
Subgrade Preparation: Leveling and compacting the foundation soil.
Geocell Deployment: Expanding and anchoring the geocell panels on the subgrade.
Filling: Infill materials such as sand, crushed stone, or recycled aggregates are placed inside the cells.
Compaction: The filled cells are compacted to form a solid, load-bearing surface.
Surface Finishing: A final layer of asphalt, concrete, or gravel may be applied, depending on road type and design requirements.
Performance Benefits
Geocell-based roads demonstrate higher load-bearing capacity, better drainage, and longer service life compared to conventional methods. They also reduce frost heave effects and subgrade deformation in cold regions, improving year-round usability.
Future Outlook
With sustainability becoming a key priority in infrastructure projects, geocell road construction is expected to see wider adoption globally. Manufacturers are focusing on producing eco-friendly materials using recycled polymers and developing geocells with greater tensile strength and thermal resistance.
Digital design tools and simulation-based engineering are also enhancing the precision and efficiency of geocell deployment, ensuring consistent performance across diverse soil conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the main materials used in geocell production?
Most geocells are made from HDPE, though polyester and polypropylene are also used for specialized applications requiring higher stiffness or chemical resistance.
2. How long does a geocell-reinforced road last?
When properly installed, geocell roads can last 20–30 years, depending on traffic load and environmental conditions.
3. Can geocells be used for temporary or emergency roads?
Yes. Their rapid deployment and easy removal make them ideal for temporary, military, or emergency road applications.
4. Are geocells suitable for extreme climates?
Absolutely. HDPE-based geocells offer excellent resistance to temperature fluctuations, UV exposure, and freeze-thaw cycles.
Conclusion
As the construction industry continues to embrace sustainable and cost-efficient technologies, geocell road construction stands at the forefront of modern infrastructure solutions. Its unique combination of strength, flexibility, and environmental performance makes it an ideal choice for diverse applications—from rural pathways to high-traffic highways.
For international buyers, engineers, and project developers seeking long-term value and stability, geocells offer a proven path toward resilient road networks.
Contact us today to learn more about geocell solutions tailored to your road construction projects.
ction.