Geomat - BPM Geosynthetics
In the environmental/infrastructural sector BPM Geomat is a very successful and versatile product with numerous applications. BPM GeomatWoven geosynthetics material is designed as a geosynthetic for soil reinforcement,combined with high tensile strength,perfect creep and creep rupture performance to meet the needs of competitive civil and environmental construction projects. Its particular construction can reach slope stabilisation, riverbank protection and surface runoff reduction representing a valuable sustainable land management practice. This paper intends to offer an extensive description of Geomat by integrating both the features and the applications, and the crucial function it has been performing for plant growing, soil protection, and water conservation dual-use in various environmental and infrastructural projects.
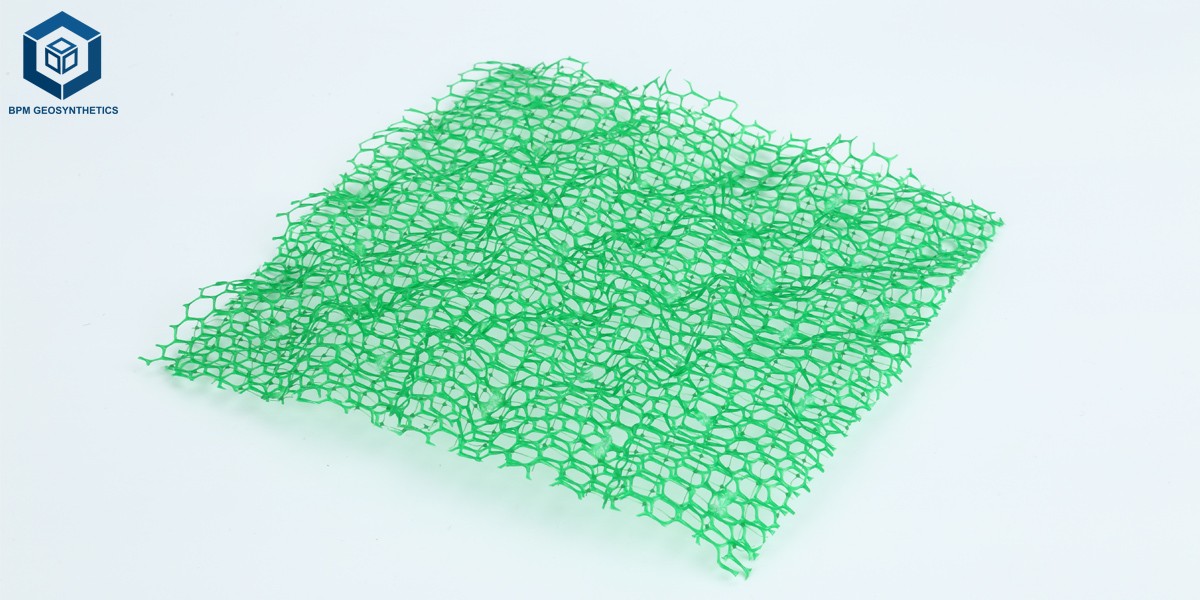
A Geomat is a three-dimensional, synthetic erosion control mat primarily used in slope protection, riverbanks, road embankments, and ecological restoration projects. It combines geotechnical engineering principles with sustainable design to provide surface stabilization and vegetation reinforcement. This article explores the structure, materials, engineering principles, standards, and applications of Geomats, as well as their installation and maintenance considerations.
What Is a Geomat?
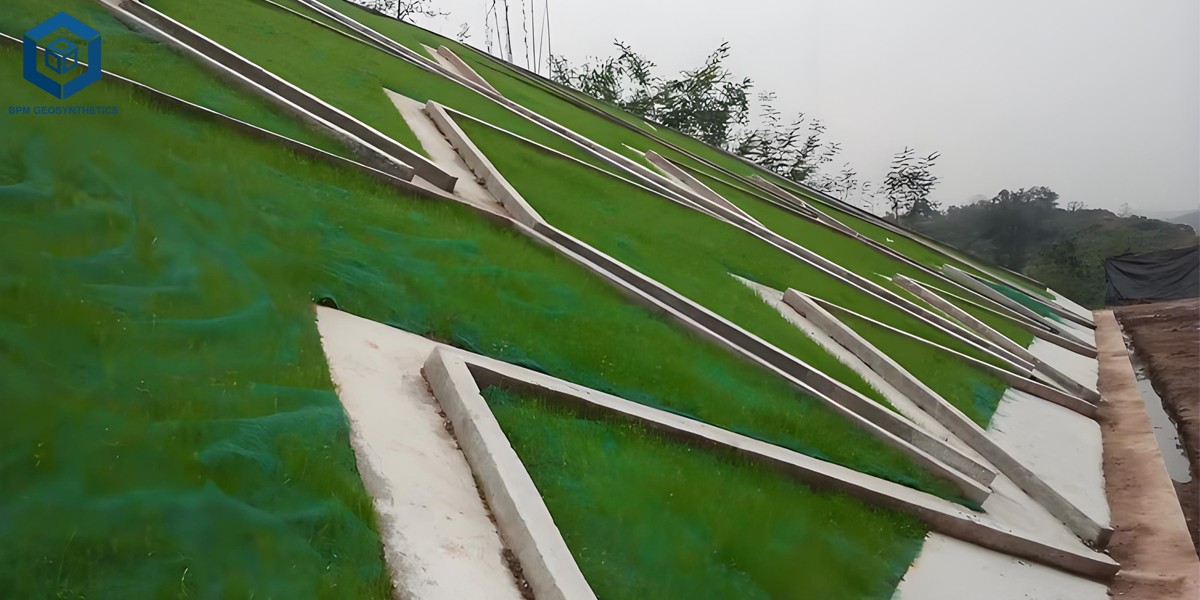
A Geomat is a flexible, lightweight geosynthetic product made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polypropylene (PP), or a combination of thermoplastic polymers. Its three-dimensional mesh structure entangles plant roots, increasing the friction and shear resistance of the soil. This design prevents surface erosion and improves slope stability.
Key characteristics include:
Porous structure: Allows vegetation growth and water infiltration.
UV resistance: Enhances durability in outdoor environments.
Chemical stability: Resists acids, alkalis, and microbial attack.
Reinforcement: Increases the bonding strength between soil and vegetation.
Engineering Principles and Function
The engineering concept behind Geomats lies in soil reinforcement and erosion control through root entanglement and surface stabilization. When installed, Geomats form an interlocking network between the mat fibers, soil particles, and plant roots.
Working mechanism:
Mechanical reinforcement: The mat stabilizes the soil surface against rain or wind erosion.
Hydraulic protection: Reduces flow velocity and prevents surface runoff from washing away the soil.
Ecological integration: Promotes plant growth, forming a composite layer of vegetation and synthetic structure.
These principles comply with geotechnical design methods used in slope engineering and hydraulic protection.
Industry Standards and Material Compliance
Geomats should conform to recognized international and national geosynthetic standards, including:
ASTM D6460 – Standard test method for erosion control performance.
ISO 13426-2 – Testing of geosynthetic reinforcement properties.
EN 13252 – Geotextiles and geotextile-related products used in drainage systems.
GB/T 18744 (China National Standard) – Technical requirements for erosion control mats.
These standards define performance parameters such as tensile strength, thickness, mass per unit area, and UV resistance, ensuring safety and reliability in engineering projects.
Applications of Geomats
Geomats are widely used in civil, environmental, and hydraulic engineering, including:
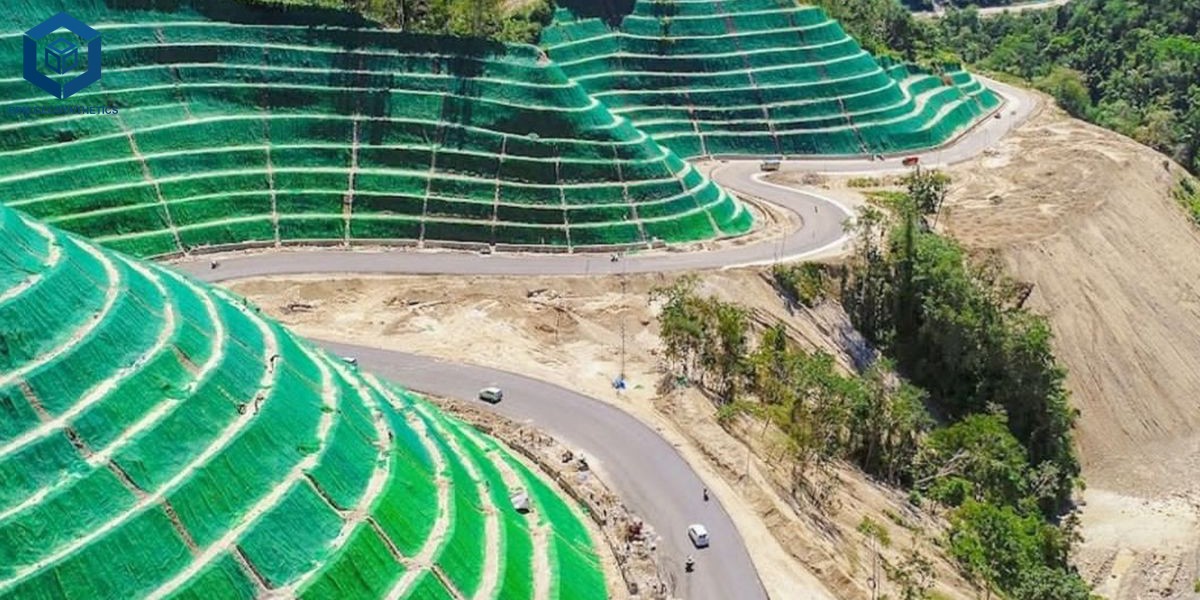
Highway and railway embankments – to prevent slope erosion.
Riverbanks and canals – for anti-scouring protection.
Reservoirs and dams – to enhance surface stability.
Coastal engineering – for shoreline and dune reinforcement.
Land reclamation and landscaping – to restore vegetation cover.
Each application requires selecting appropriate mat grades (Erosion Control Class I–III) based on slope steepness, rainfall intensity, and soil characteristics.
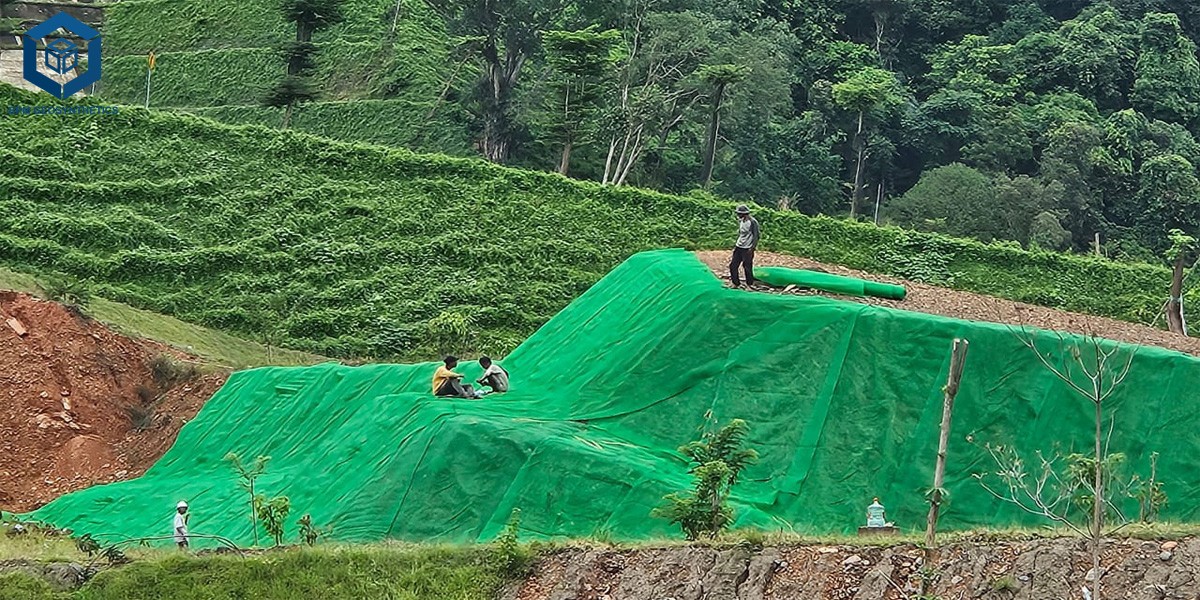
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation ensures long-term performance:
Site preparation: Remove debris and level the soil surface.
Anchoring: Fix the Geomat at the top of the slope using steel nails or anchor rods.
Laying: Overlap edges by 10–15 cm to prevent gaps.
Seeding: Spread grass seeds uniformly before or after installation.
Soil cover: Apply 1–2 cm of fine soil to enhance seed contact.
Watering and maintenance: Regular watering promotes vegetation establishment.
Incorrect installation may lead to uneven surface settlement or insufficient root bonding, reducing its effectiveness.
Performance Advantages
Geomats provide superior erosion resistance, strong soil-plant reinforcement, and excellent ecological compatibility. Their lightweight design ensures easy transport and installation, significantly reducing construction time and cost. With high UV and chemical resistance, they deliver long-term durability under harsh environmental conditions. By integrating vegetation, Geomats transform artificial slopes into natural green landscapes, improving aesthetics and biodiversity. Complying with international standards, they offer reliable mechanical strength, effective drainage performance, and environmentally sustainable protection, making them an ideal solution for modern civil and ecological engineering projects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How long does a Geomat last?
Typically 5–10 years, depending on UV exposure and maintenance, after which the vegetation layer takes over natural protection.
2. Can Geomats be used on steep slopes?
Yes. With proper anchoring and soil bonding, they can stabilize slopes up to 60 degrees.
3. Are Geomats environmentally friendly?
Yes. They promote vegetation growth and reduce soil erosion without harming the ecosystem.
4. What’s the difference between Geomat and Geocell?
Geomats provide surface erosion control, while Geocells offer structural reinforcement for deeper soil stabilization.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
When selecting and installing Geomats, engineers must follow:
Environmental impact assessments (EIA) before slope construction.
Construction codes for geotechnical and hydraulic structures.
Safety protocols to prevent soil slippage during installation.
Compliance ensures both engineering safety and ecological sustainability.